- Openpgp For Windows
- Java Openpgp
- Openpgp.js Generate Key Pair Linux
- Openpgp.js Generate Key Pair Number
- Table of Contents
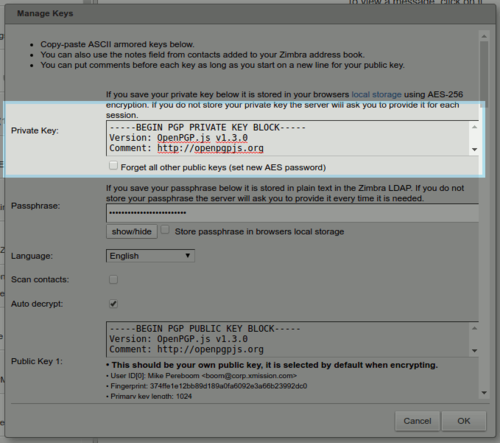
- Generating a new keypair
- Exchanging keys
- Encrypting and decrypting documents
- Making and verifying signatures
GnuPG is a tool for secure communication.This chapter is a quick-start guide that covers the core functionalityof GnuPG.This includes keypair creation, exchanging and verifying keys, encryptingand decrypting documents, and authenticating documents with digitalsignatures.It does not explain in detail the concepts behind public-key cryptography,encryption, and digital signatures.This is covered in Chapter 2.It also does not explain how to use GnuPG wisely.This is covered in Chapters 3 and 4.
GnuPG uses public-key cryptography so that users may communicate securely.In a public-key system, each user has a pair of keys consisting ofa
The command-line option
The OpenPGP.js project aims to provide an Open Source OpenPGP library in JavaScript. Use the generateKey method of the SubtleCrypto interface to generate a new key (for symmetric algorithms) or key pair (for public-key algorithms). Syntax const result = crypto.subtle.generateKey( algorithm, extractable, keyUsages ). Apr 12, 2018 By default ssh-keygen will create a 2048-bit RSA key pair, which is secure enough for most use cases (you may optionally pass in the -b 4096 flag to create a larger 4096-bit key). After entering the command, you should see the following output.
You must also choose a key size.The size of a DSA key must be between 512 and 1024 bits, and an ElGamalkey may be of any size.GnuPG, however, requires that keys be no smaller than 768 bits.Therefore, if Option 1 was chosen and you choose a keysize larger than1024 bits, the ElGamal key will have the requested size, but the DSAkey will be 1024 bits.
If you don't already have an SSH key, you must generate a new SSH key. If you're unsure whether you already have an SSH key, check for existing keys. If you don't want to reenter your passphrase every time you use your SSH key, you can add your key to the SSH agent, which manages your SSH keys and remembers your passphrase. Generating a new SSH key. OpenPGP.min.js doesn't generate key pair. Ask Question Asked 4 years, 11 months ago. Active 4 years, 11 months ago. Viewed 899 times 1. I'm since yesterday trying to make the openpgp.js work. I tried the full version, but no success, so right now I.
Openpgp For Windows
Finally, you must choose an expiration date.If Option 1 was chosen, the expiration date will be used for both theElGamal and DSA keypairs.
You must provide a user ID in addition to the key parameters.The user ID is used to associate the key being created with a realperson.
GnuPG needs a passphrase to protect the primary and subordinate private keys that you keep in your possession.
After your keypair is created you should immediately generate a revocationcertificate for the primary public key using the option
Java Openpgp
Notes
[1]Option 3 is to generate an ElGamal keypair that isnot usable for making signatures.
Several tools exist to generate SSH public/private key pairs. The following sections show how to generate an SSH key pair on UNIX, UNIX-like and Windows platforms.
Generating an SSH Key Pair on UNIX and UNIX-Like Platforms Using the ssh-keygen Utility
UNIX and UNIX-like platforms (including Solaris and Linux) include the ssh-keygen utility to generate SSH key pairs.
- Navigate to your home directory:
- Run the ssh-keygen utility, providing as
filenameyour choice of file name for the private key:The ssh-keygen utility prompts you for a passphrase for the private key.
- Enter a passphrase for the private key, or press Enter to create a private key without a passphrase:
Note:
While a passphrase is not required, you should specify one as a security measure to protect the private key from unauthorized use. When you specify a passphrase, a user must enter the passphrase every time the private key is used.
The ssh-keygen utility prompts you to enter the passphrase again.
- Enter the passphrase again, or press Enter again to continue creating a private key without a passphrase:
- The ssh-keygen utility displays a message indicating that the private key has been saved as
filenameand the public key has been saved asfilename.pub. It also displays information about the key fingerprint and randomart image.
Generating an SSH Key Pair on Windows Using the PuTTYgen Program
The PuTTYgen program is part of PuTTY, an open source networking client for the Windows platform.
Openpgp.js Generate Key Pair Linux
Openpgp.js Generate Key Pair Number
- Download and install PuTTY or PuTTYgen.
To download PuTTY or PuTTYgen, go to http://www.putty.org/ and click the You can download PuTTY here link.
- Run the PuTTYgen program.
- Set the Type of key to generate option to SSH-2 RSA.
- In the Number of bits in a generated key box, enter 2048.
- Click Generate to generate a public/private key pair.
As the key is being generated, move the mouse around the blank area as directed.
- (Optional) Enter a passphrase for the private key in the Key passphrase box and reenter it in the Confirm passphrase box.
Note:
While a passphrase is not required, you should specify one as a security measure to protect the private key from unauthorized use. When you specify a passphrase, a user must enter the passphrase every time the private key is used.
- Click Save private key to save the private key to a file. To adhere to file-naming conventions, you should give the private key file an extension of
.ppk(PuTTY private key).Note:
The.ppkfile extension indicates that the private key is in PuTTY's proprietary format. You must use a key of this format when using PuTTY as your SSH client. It cannot be used with other SSH client tools. Refer to the PuTTY documentation to convert a private key in this format to a different format. - Select all of the characters in the Public key for pasting into OpenSSH authorized_keys file box.
Make sure you select all the characters, not just the ones you can see in the narrow window. If a scroll bar is next to the characters, you aren't seeing all the characters.
- Right-click somewhere in the selected text and select Copy from the menu.
- Open a text editor and paste the characters, just as you copied them. Start at the first character in the text editor, and do not insert any line breaks.
- Save the text file in the same folder where you saved the private key, using the
.pubextension to indicate that the file contains a public key. - If you or others are going to use an SSH client that requires the OpenSSH format for private keys (such as the
sshutility on Linux), export the private key:- On the Conversions menu, choose Export OpenSSH key.
- Save the private key in OpenSSH format in the same folder where you saved the private key in
.ppkformat, using an extension such as.opensshto indicate the file's content.